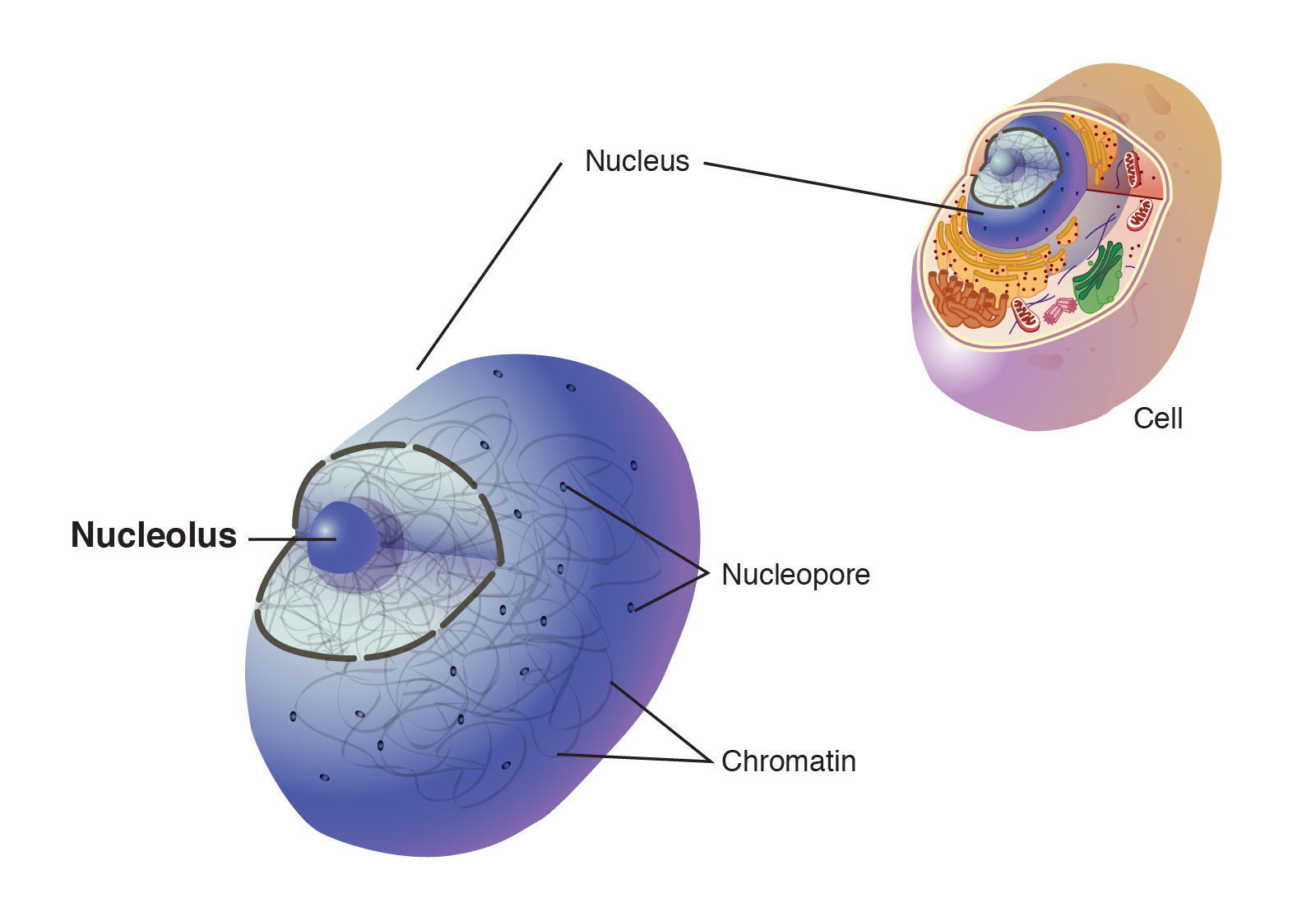
Describe Briefly the Functions of the Nucleus and the Nucleoli
The nucleus consists of other structures such as the nuclear membrane nucleoplasm nucleolus and chromosomes. It is responsible for storing the cells hereditary material or the DNA.

The Nucleus And Dna Replication Anatomy And Physiology I
It synthesizes rRNA and assembles ribosomes in the nucleus.
. Nucleus is one of the most important components of the cell. It then transfers the subunits out to the bottom of the cell where they merge into intact ribosomes. Nucleus contains majority of cells genetic material.
If the nucleus is removed the cell ultimately dies. It is involved in transmission of hereditary characters from parents to off springs. The substance of a cell nucleus consisting of strands of DNA RNA and various proteins that forms chromosomes during cell division.
It is responsible for coordinating many of the important cellular activities such as protein synthesis cell division growth and a host of other important functions. These products are key in the synthesis of proteins which are the basic building blocks of all biological tissue. Photosynthetic organelle converts sunlight energy to chemical energy stored in sugar molecules.
The main function of the nucleolus is in the production of ribosomes and synthesis of ribosomal RNA rRNA. Mitochondrion is where cellular respiration occurs and most ATP if generated. There are usually one to several nucleoli within the nucleus.
DNA determines both the structure and function of cells and heredity b Nucleoli. Highlight the functions of the nucleus. This involves regulating gene expression initiating cellular reproduction and storing genetic material necessary for all of these tasks.
The primary function of the nucleolus consists in ribosomal RNA rRNA transcription rRNA processing and ribosome subunit assembly Hernandez-Verdun et al. Nucleolus nucleoli A cluster of protein DNA and RNA that is not enclosed by a membrane. Stereo view of a triple-labeled HeLa cell nucleus showing the localization of coiled bodies green GFP-coilin PML bodies red autoimmune serum recognizing SP100 and.
Nucleus of a cell and mitochondria. The nucleus is a cell organelle which is spherical and is present in all the eukaryotic cells. Nucleoli vary in size in different cells for example in small cells like yeast they are 10 μm in diameter The nucleolus is a dynamic membrane-less structure whose primary function is.
Chromatin is a material that consists of DNA and proteins. Within these parts the nuclear envelope is the membrane enclosing the nucleus and continuous with ER. Nucleus It coordinates cell activities like protein synthesis and cell division Nucleoli It takes part in the production of subunits that unites to form ribosomes.
Nuclear envelope nucleolus and chromatin. 7 Describe briefly the functions of the nucleus and the nucleoli. The nucleolus whose key function is to hold ribosomes together is the main structure in the cell nucleus.
The nucleus contains the genetic material of the cell in the form of DNA which codes for messenger RNA which in turn provides instructions for the synthesis of proteins. Proteins produced in the cytoplasm move through the nuclear pores into the nucleus and to the nucleolus. The key function of the nucleus is to control cell growth and multiplication.
Nucleus - Surrounded by the nuclear envelope. The nucleus is a site for transcription in which messenger RNA mRNA are produced for protein synthesis. Storage of proteins and RNA ribonucleic acid in the nucleolus.
It then sends the subunits out to the rest of the cell where they combine into complete ribosomes. The nucleus has three main parts. It is not surrounded by a membrane but sits in the nucleus.
Functions of DNA molecules. Ribosomes produce proteins hence the nucleolus performs an important function in producing proteins in the cell. The nucleolus controller regions of chromosomes which harbor the genetic factor for prerRNA are the basis for the nucleolus.
Including the proteins that make up part of the ribosomes DNA also code for ribosomal RNAs which are combined with proteins in the nucleolus into the subunits of ribosomes. All active nucleoli comprise two ultrastructure constituents the nucleolus thick febrile constituent. Nucleus is referred to as the control centre of the eukaryotic cells.
Describe briefly the functions of the nucleus and nucleoli. Some nuclei plural of nucleus may contain meany nucleoli plural of nucleolus. It is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell s hereditary information and controls the cells growth and reproduction.
8 Name three kinds of micrograph used in this book to illustrate cell structures. Nucleolus is a non membranous structure involved in production of ribosomes. A Light Microscope Transmission electron microscope and scanning electron.
The nucleolus is the largest and most prominent domain in the eukaryotic interphase cell nucleus. Nucleolus A small round granular body composed of protein and RNA in the nucleus of a cell. It controls cell division.
During the cell division chromatins are arranged into chromosomes in the nucleus. The nucleus has 2 primary functions. It also helps in the coordination of both the genes and the gene expression.
Nucleoli are present in almost every eukaryotic cell type and represent the most prominent compartment of the cell nucleus. The nucleolus fabricates subunits of ribosomal from proteins and RNA which is also perceived as rRNA. It controls the various metabolic activities of the cell.
Organized as DNA molecules along with a variety of proteins to form chromosomes. In order for a nucleus to carry out important reproductive roles and other cell activities it needs proteins and ribosomes. Some cells such as muscle cells contain more than one nucleoli.
The subunits of ribosomes a type of cytoplasmic organelle are formed within a nucleolus. Production of ribosomes protein factories in the nucleolus. The nucleolus makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and ribosomal RNA also known as rRNA.
The nucleolus is a round body located inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. Therefore it is called the control centre of the cell. Nucleoli - are diffuse bodies with no surrounding membrane that are found within the nucleus.
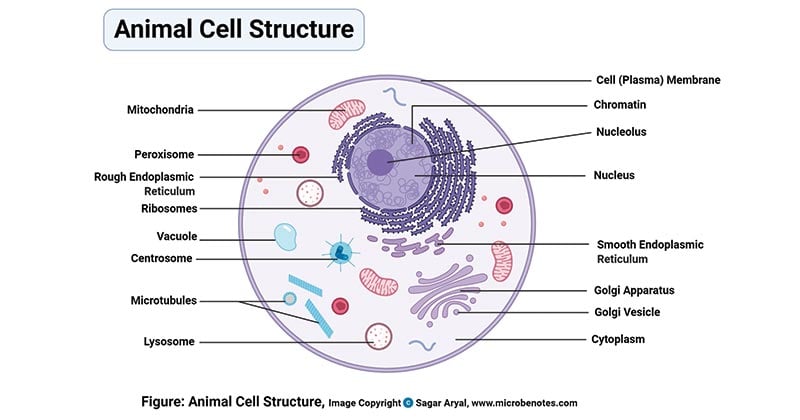
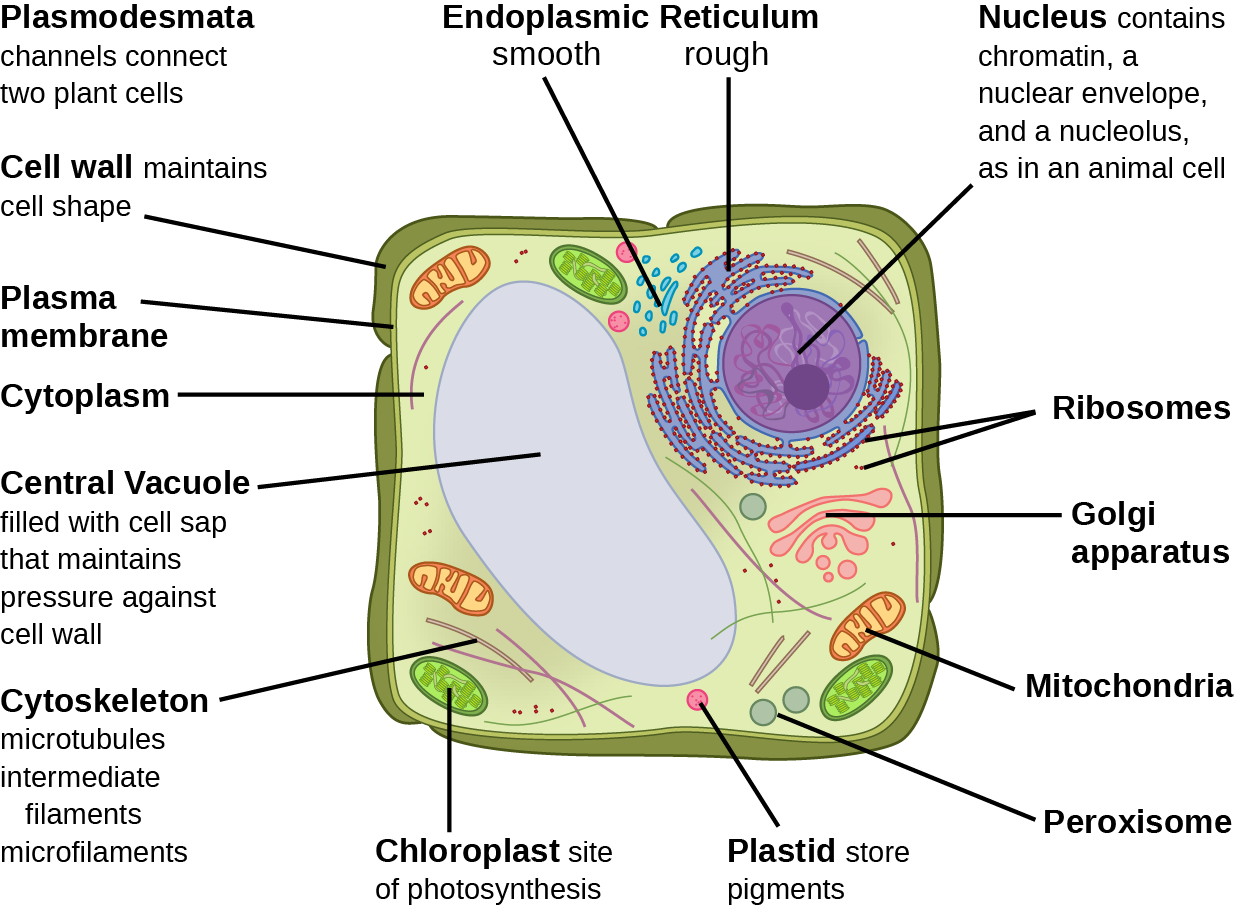
Animal Cell Definition Structure Parts Functions Labeled Diagram
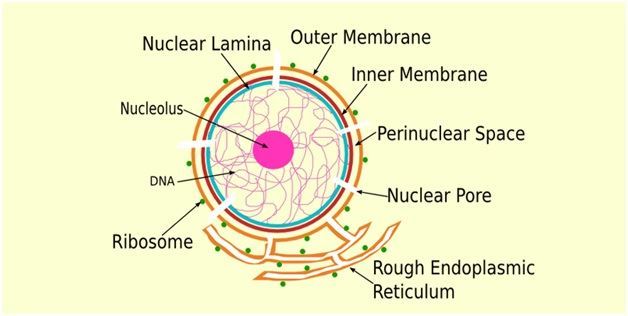
Nuclear Membrane Structure Function Of Nuclear Membrane

Nucleus Definition Structure Function With Diagram
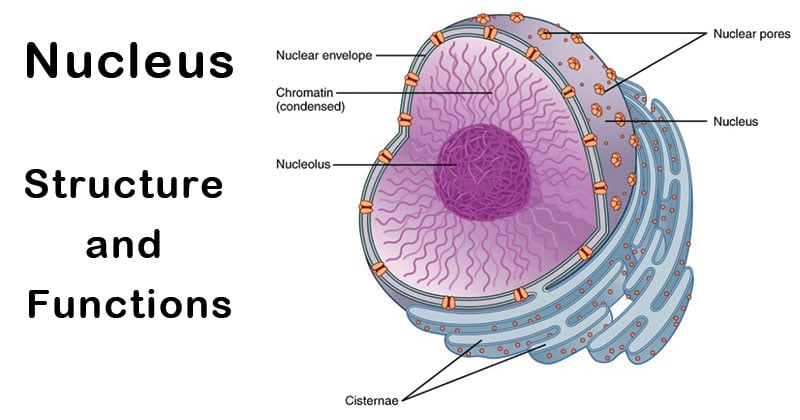
Nucleus Definition Structure Parts Functions Diagram
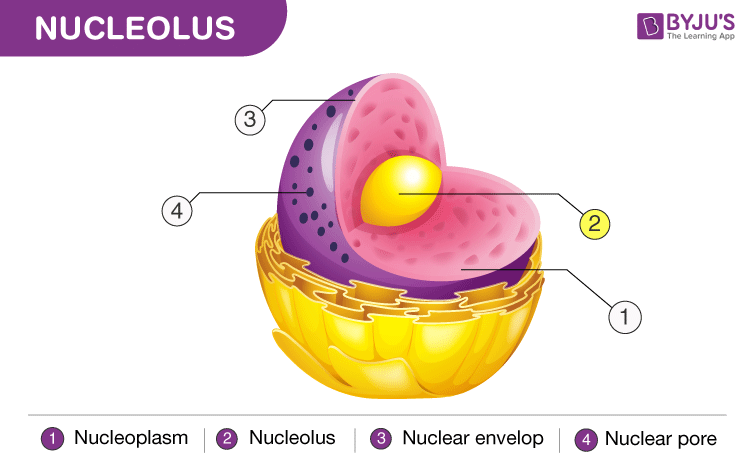
Nucleolus Function Difference Between Nucleus Nucleolus

Structural And Functional Domains Of The Nucleolus Fc Fibrillar Download Scientific Diagram
Nucleus Cell Nucleus Nucleus Structure And Functions
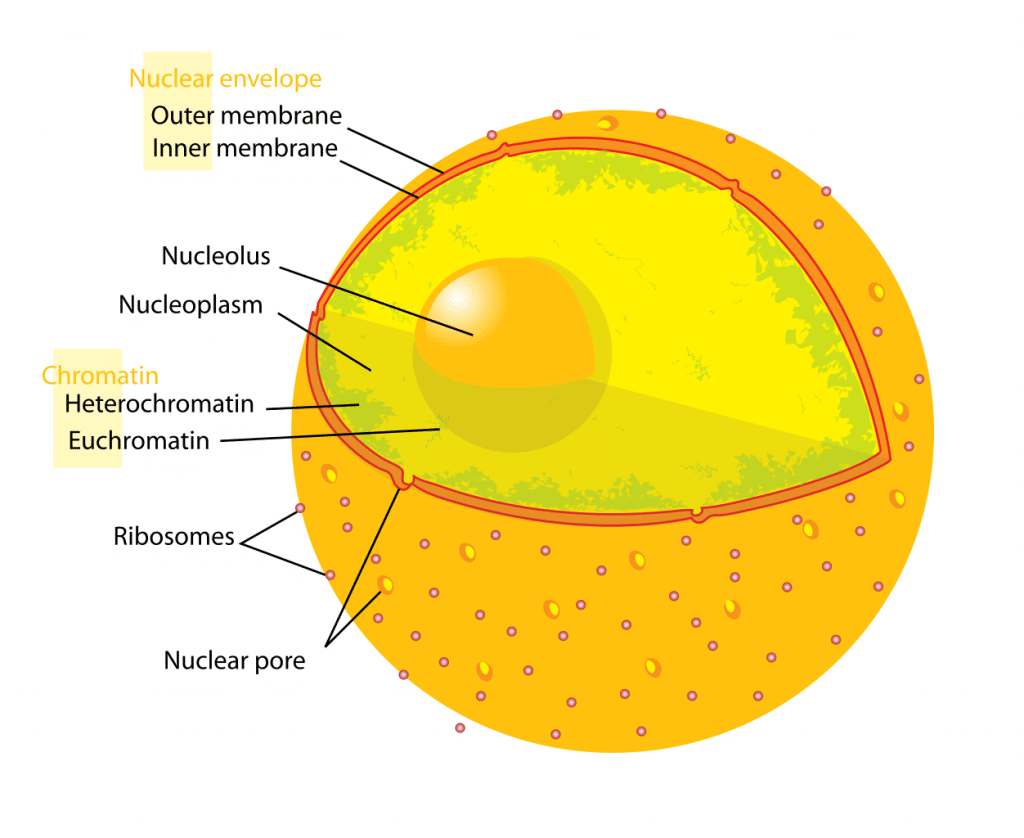
Nucleus Structure Function Euchromatin Teachmephysiology
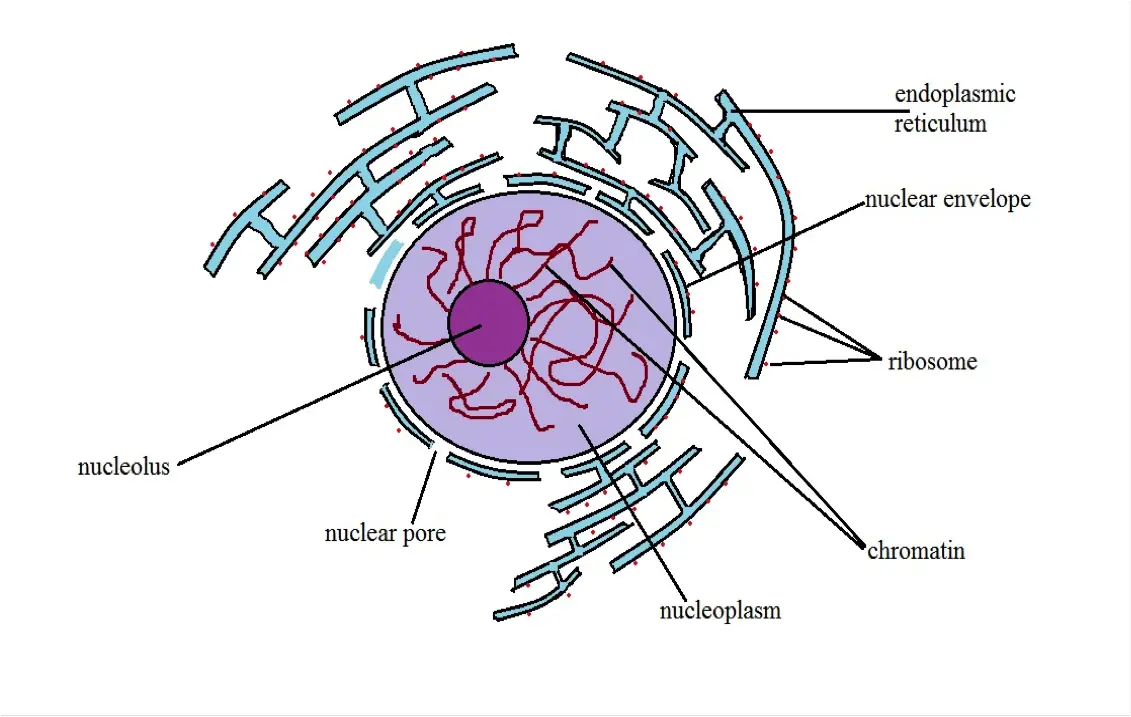
Nucleus Definition Structure Function Cellular Vs Atomic Nuclei
What Is The Function Of The Nucleus In A Cell Quora

5 Main Parts Of Nucleus Biology
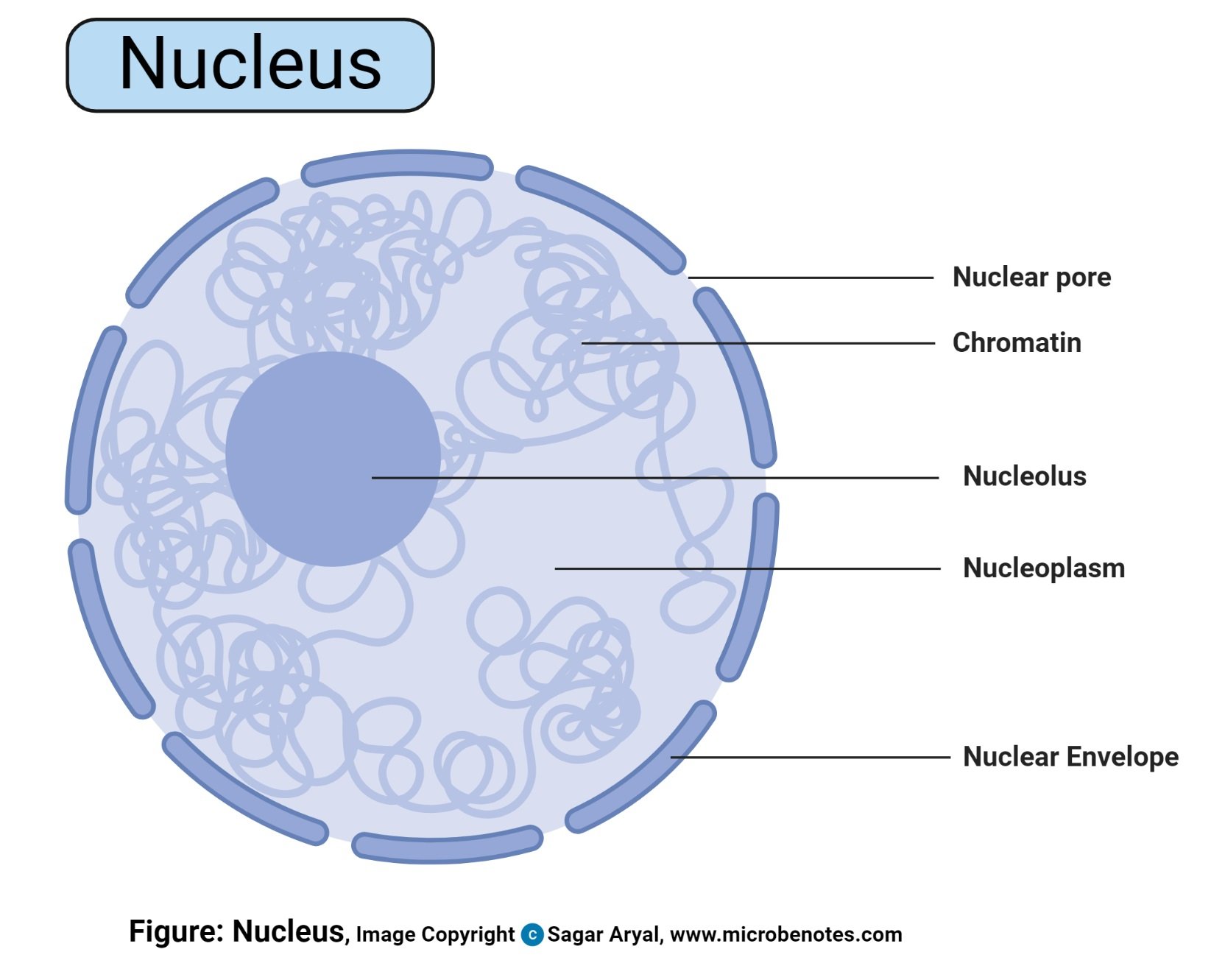
Nucleus Definition Structure Parts Functions Diagram
What Is The Function Of The Nucleus In A Cell Quora
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nucleolus/cpz4j9r1x6VuyNmmbgdA_Nucleolus.png)
Cell Nucleus Histology Structure And Functions Kenhub
What Is The Function Of The Nucleus In A Cell Quora
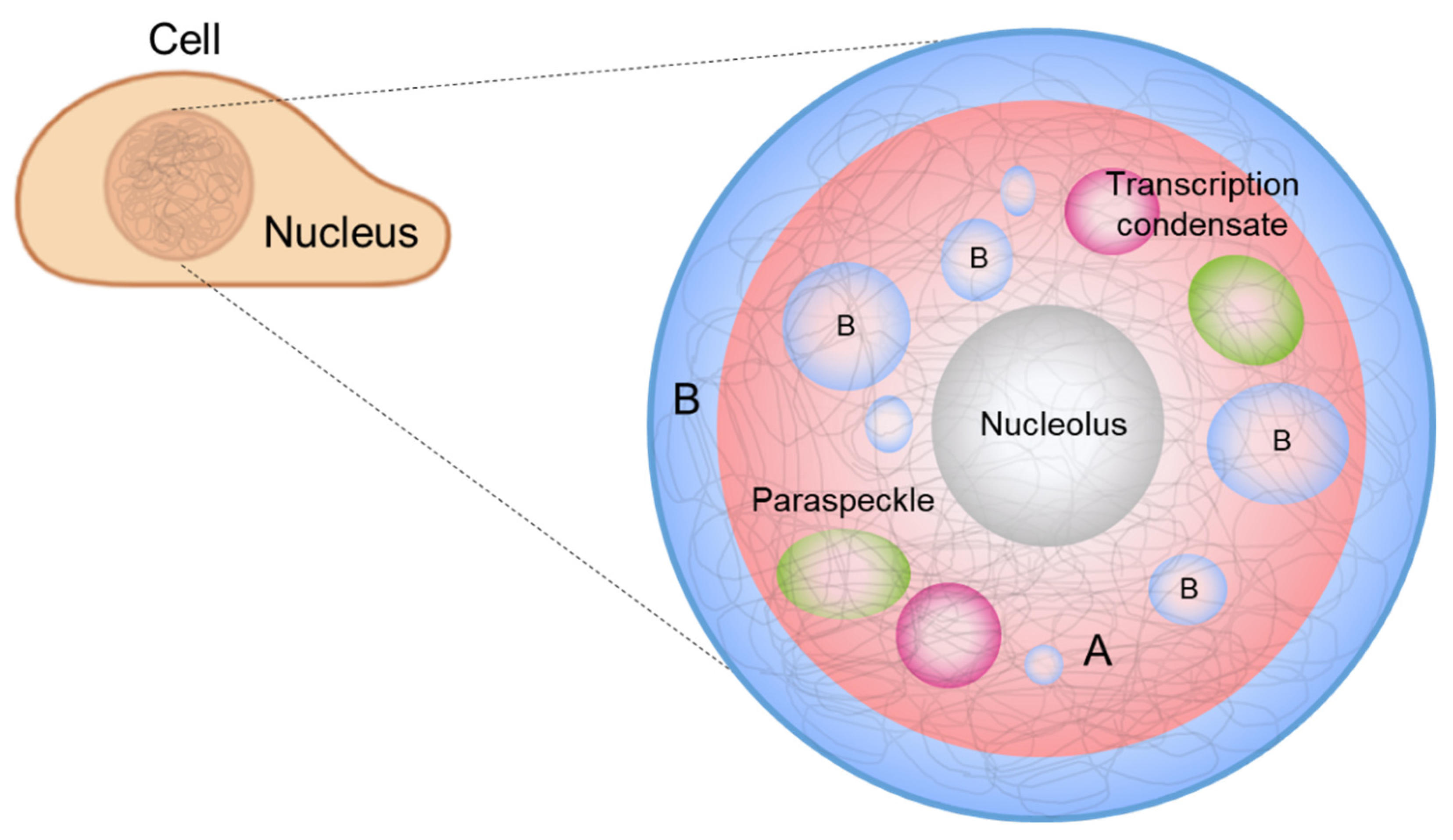
Ijms Free Full Text Current Understanding Of Molecular Phase Separation In Chromosomes Html

Comments
Post a Comment